
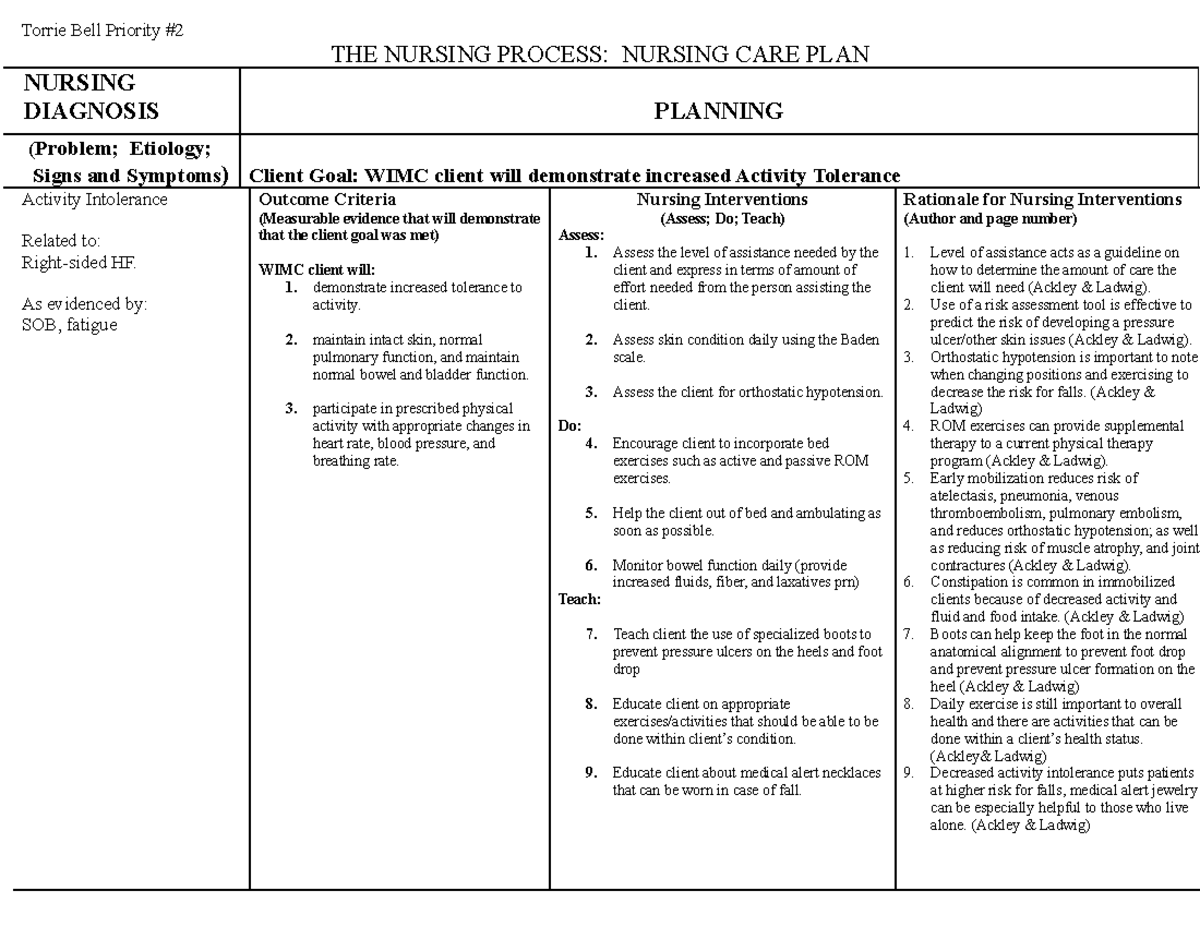
Steroids – to slow down the damage of the joints, reducing inflammation and pain.Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.Depending on the severity of RA, doctors can prescribe:

Imaging – X-ray of the affected joints MRI and ultrasound to determine the severity Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis.Blood tests – Complete blood count to check for increased ESR and CRP specific blood tests for rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibodies.Physical exam – to check for the signs and symptoms such as joint redness, swelling, or warmth, as well as muscular strength and reflex exams.The wrists may also be affected by RA, causing them to be inflamed and compress the median nerve that innervates the hand and fingers. RA patients are at risk for developing this disorder, which reduces the moisture in the eyes and oral mucosa, resulting to dryness. Aside from the affected joints, the nearby bones can eventually weaken, making the patient at a high risk for developing fractures. If they rupture in the lungs, collapsed lung may follow. They can be dangerous as these nodules can also form in the lungs.
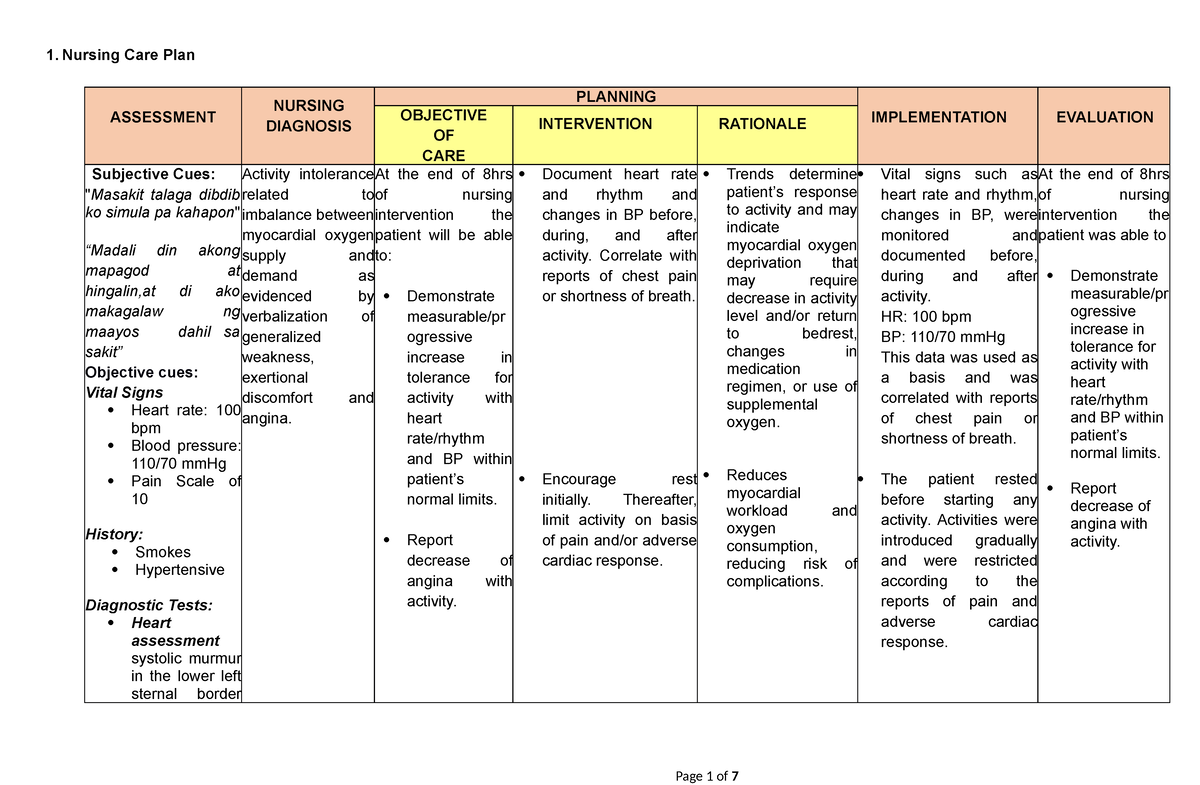
RA puts a person at risk of developing rheumatoid nodules, which are firm clumps of tissue that form around the elbows, or other pressure points.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
